Debate On Fundamental Rights And Directive Principles
They are considered as positive rights as they impose positive obligations on the state.
Debate on fundamental rights and directive principles. It is indeed a test of the structure on which a certain society has been built its aspirations and the coherent principles involved in realising the necessary moral code. This continued for a decade and half and some other cases such as qureshi v s state of bihar sajjan singh v s state of rajasthan cases court confirmed this stand. This means that fundamental rights were given superiority over the directive principles. Core difference between fundamental rights and directive principles of state policy is of justifiability.
In the landmark judgment of state of madras vs. While rights and duties are fundamental and go to the root of how a citizen behaves or acts in the society the other is a guideline for the state to create and pass laws. According to the amendment of 1971 any law that even though it deviates from the fundamental rights but has been made to give effect to the directive principles in article 39 b c would not be deemed invalid. In case of violation of fundamental rights one can move to high court or supreme court but in case of violation non implementation.
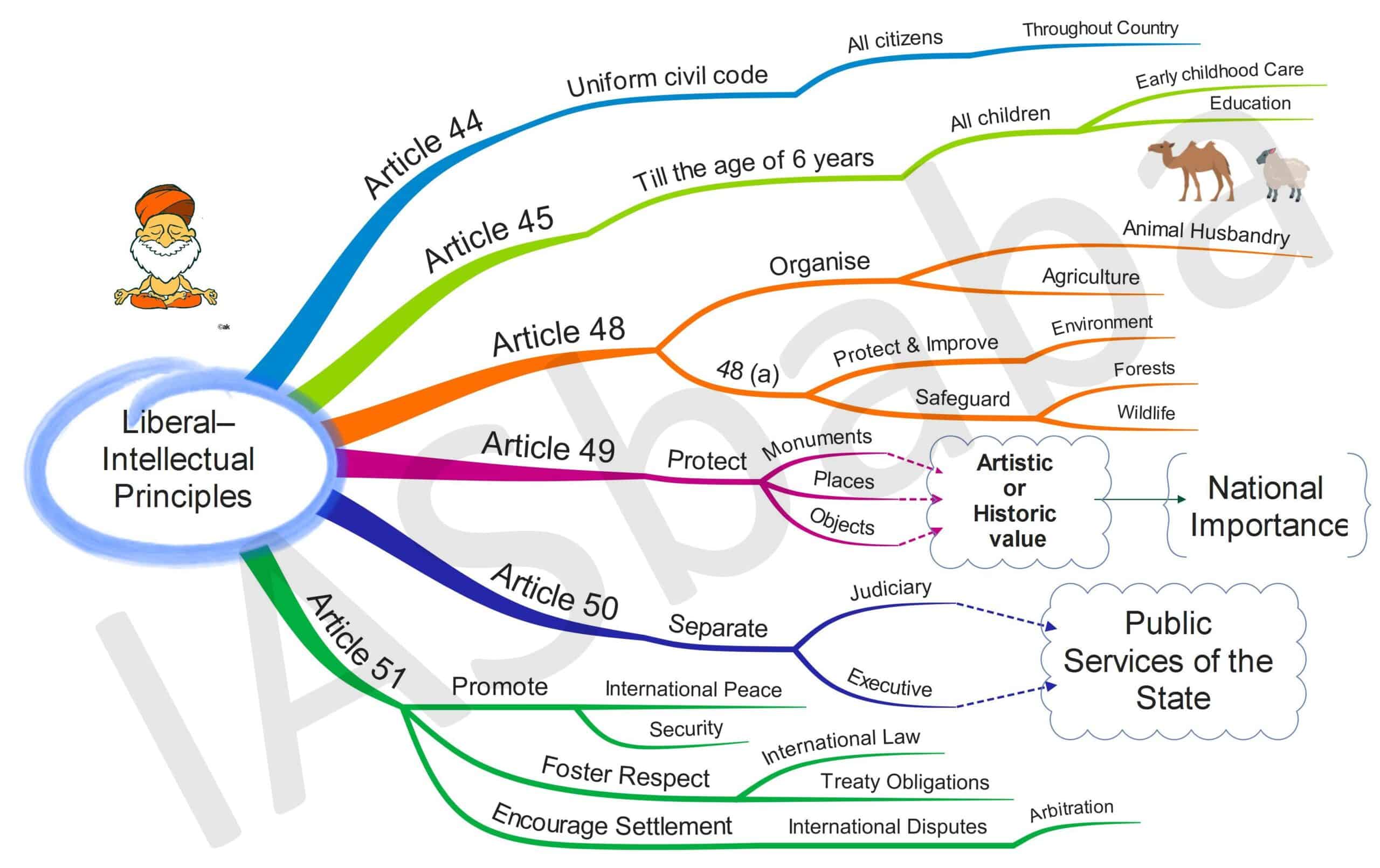
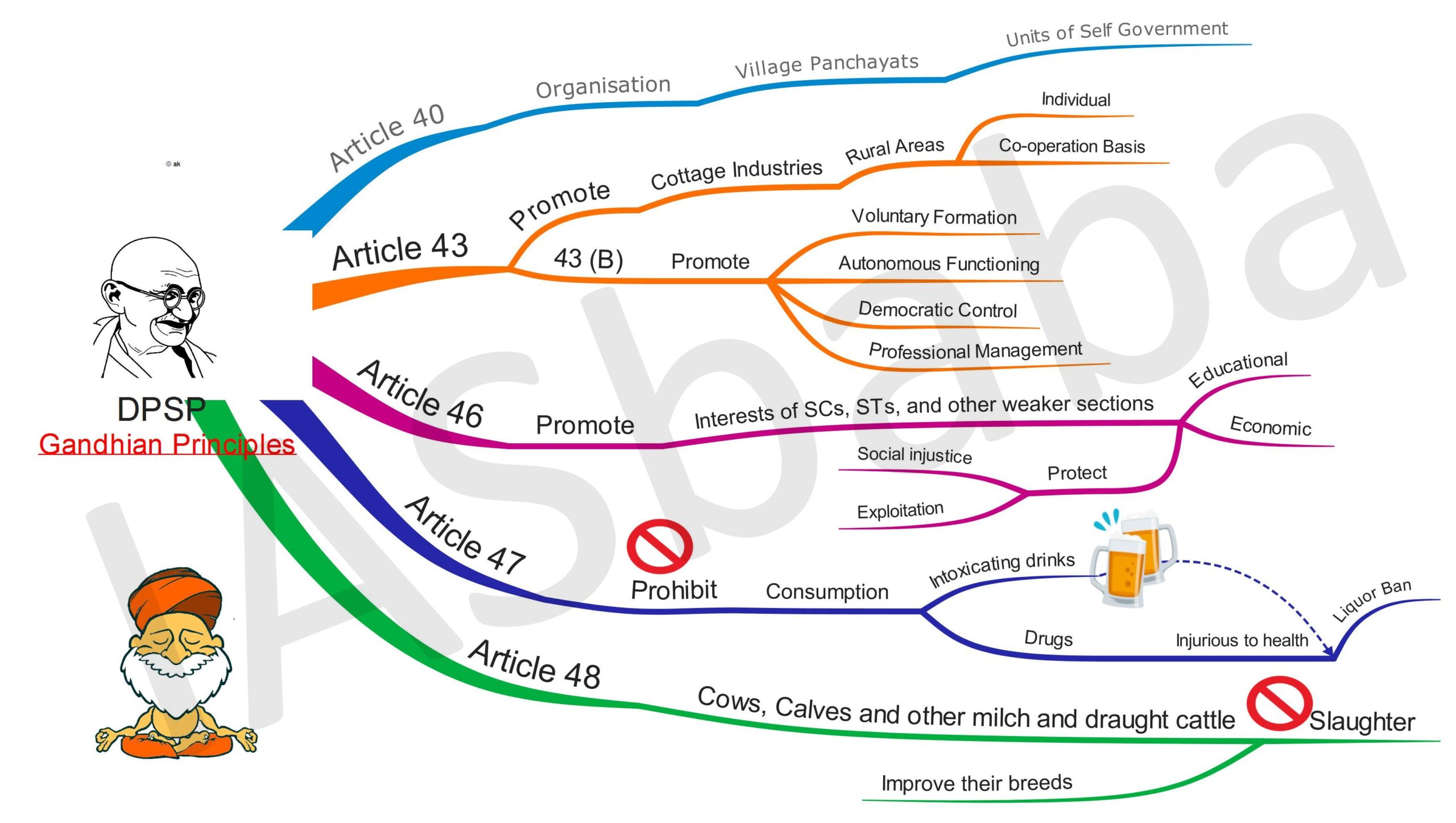
Directive principles of state policy part iv of the constitution deals with the directive principles of state policy. In the kesavananda bharati v state of kerala case in 1973 the supreme court overruling a previous decision of 1967 held that the fundamental rights could be amended subject to judicial review in case such an amendment violated the basic structure of the. The fundamental rights fundamental duties and directive principles are two sides of a coin that serve one purpose the interest of the citizen. Thus it is relevant to discuss the directive principles of state policy dpsps provided for in the indian constitution in part iv articles 36 51 which lay down principles for the achievement of this social and economic justice.
Srimathi champakam which subsequently led to the 1st constitutional amendment justice das stated that directive principles were expressly made unenforceable by article 37 and therefore could. The relationship between directive principles and fundamental rights has been a story of debate ever since their inception. They are non justifiable in nature yet they are important to provide. About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy safety how youtube works test new features.